Public companies are required to share their performance regularly to their investors. The way they do that is through annual reports and other fillings.
An annual report is a financial and operational overview for a public company. It is prepared for investors, employees, lenders, and the general public. The annual report works as a guidance for investors and lenders to take decision.
It is divided into two main sections. The cover page, and the SEC 10-K form.

Let us look at each section and its sub-sections in details.
First Section: Cover Page
The beginning section of the annual report looks graphically appealing and has overall summary about the company.
Just note that this section communication is usually positive. You should be careful when analysing it and treat it as marketing material.
To make it easier for you guys reading each part of an annual report there will be a number next to each one.
-
Key Company Highlights
The first thing you will see in an annual report is selected company highlights.
Companies highlights will present how well they performed. for example, they will share their historical revenues, profit margins, net income, and other industry related figures.
If it was a restaurant chain like The Cheesecake Factory, other related figures they show is the total number of restaurant branches they are operating.
-
Chairman’s Letter to Shareholders
The letter to shareholders describes the business situation, key achievements/challenges, strategic decisions taken.
It is a reflection of the company situation, strategic point of view, and business personality.
You can imagine this section as a conversation with the chairman discussing the company.
-
CEO Message
The CEO message is more specific compared to the chairman’s letter section.
It discusses strategies that the company is taking and share figures of their achievements and their targets
In general, the cover page section of the annual report is like a sales pitch of the business.

Just a note to you guys, if you plan to analyse this section just make sure to have a look at the recent annual reports chairman’s and CEO letters. Ask yourself “did what they promise at the cover have been delivered?”
The upcoming section of the annual report is more regulated. It is a form submitted to the US securities and exchange commission (SEC) a government regulatory agency.
Second Section: SEC 10-K form
To protect investors from misrepresented information, there is an entity called the US securities and exchange commission that oversee what companies are reporting.
The “10-K” form is attached after the cover page in the annual report, it covers the majority of the document and discusses business and market overview, financials, management, and any other remaining aspect related to the company.
Here is a link to their official website with the details about the form for your reference.
For you guys who are enjoying reading it here, let us carry on discussing the other elements of an annual report.
-
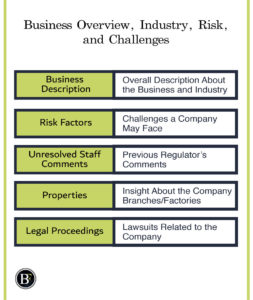
Business Description
This part will provide the overall description of the business. It will includes general information like the company:
- Legal name and location
- Some history
- Position in the market
- Business operations, legal details…etc
The idea of the business description section is that it provide an overall explanation about the business and industry.
-
Risk Factors
After discussing the company information which mostly positive. In this part, they will discuss challenges the company may face.
Risk factors talks about how sensitive is the company to market fluctuation, the risk associated to any possible damage to their brand image, changing in product/service related prices, or information system failures.
It will also discuss matters that are not directly related to the like risk associated for owning the company stock.
-
Unresolved Staff Comments
When SEC staff have unresolved comments about a company’s financials, the companies report it in the unresolved staff comments part.
Unresolved staff comments along with the risk factors section should make you aware of the risk aspect of the company.
-
Properties
This part have information about company branches/factories like their locations. It also includes the number of properties they have.
-
Legal Proceedings
If there is any lawsuits related to the company then this is where they talk about it.
The business overview part is where you can see the reality about the company, industry and the associated risk.
It can be a boring section to read in an annual report. But if you read this section from multiple companies reports you will accumulate strong industry specific knowledge.
-
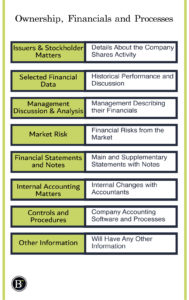
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
This part provides details about the shares activity. For example, number of shares of the company, a table of how many stocks they repurchased.
It is also provides a comparison of the share price to other benchmarks indices like the S&P 500 for example.
-
Selected Financial Data
Selected financial data provides 5-year performance and discussion about the company.
It helps you have a strategic view when analysing the financials.
-
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
After looking at the 5-year figures, the management discussion will present to you what strategies the company is taking.
Unlike the overview section at the beginning, this section will further discuss historical information and will include discussion on the percentage changes. It will also cover some trends on the markets that are influencing these changes.
The management discussion will also present the different segments of revenue and the story behind its growth/decline.
This part may look different from company to company and also from industries. But the idea behind reading is it makes you feel as if the management is reading to you their financials and letting you know what they want to say.
-
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
After knowing the financial description of the business. now this section will talk about the financial risks from the market.
For example, a company may disclose their exposure to the interest rates, currencies, commodities, and equity prices
-
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Financial statements part is the most common reference readers go to.
At the beginning, It includes a third-party auditors letter sharing their about the financials and whether they are reported according to the regulatory requirements.
Meeting the standards in the US refer to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), here is a link to their official site if you want to know more.
Along with the auditors opinions, this part includes financial statements which are the balance sheet, income statement, cashflow statement, the supplementary notes.
This part is where you can analyse the business financials objectively from the financials. Also the supplementary notes provides you further details and calculations of certain line items.
If you want to read more about the financial statement, I would recommend checking our other post about the different types of financial statements.
-
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Here you will see if there was any changes or disagreements with accountants within the company.
It can be an indicator to be aware of because it is a possibility of something wrong happening between accountant(s) and the company internally.
-
Controls and Procedures
Companies will share how they deal with their accounting software, their management take on it, and what are the limitations. It also may include updates like if a business did an acquisition how would they deal with the situation for example.
It basically discuss how they handle the accounting procedures.
-
Other Information
This part is a place holder for remaining details that fit any other section.
-
Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
This part discusses the background of the company directors and how they have been implementing code of ethics. In other words, how are they performing business with integrity.
-
Executive Compensation
This part discuss the company executives structure of compensation and their setup.
-
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
How much ownership the management hold and how many shares are there for equity compensation plan.
It provide you with an idea how much skin in the game management have. furthermore, it show the amount of dilution an existing shareholder will take if employee compensation was exercised.
-
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
This part disclose if the management have any relation with transactions the company is doing. And answers the question “is the company dealing with one of the shareholders as a client?”
It allows you make sure that the company is conducting its action with the best interest of stakeholders and not certain management parties
-
Principal Accounting Fees and Services
This part requires the companies to disclose how much they are paying their auditors. It also have some statement how the auditors are independent entity than the company itself.
-
Financial Statement Schedules
The final part is like an appendix it will have several lists like the financial statements used.

Final Thought
The annual report provides an overall information about a business. It could arguably be the best source to have information about the business particularly and have idea about the industry in general.
In summary you can see that the cover section is like a marketing material. While on the other hand the SEC 10-K form section is a sequence business follow to make it easily comparable while avoiding any misrepresentation in the shared information.
Related Posts:
- 3 Types of Financial Statements Explained
- The 3 Components of the Balance Sheet Explained
- Common Components of Income Statements Explained
Disclaimer: Above links are affiliate links and at no additional cost to you. I may earn a commission. Know that I only recommend products, tools, services and learning resources I’ve personally used and believe are genuinely helpful and relevant. It is not because of the small commissions I make if you decide to purchase them. Most of all, I would never advocate for buying something that you can’t afford or that you’re not yet ready to implement.