As a person who prefers long term investing, I am not very keen about speculative type of investment which I thought investing in cryptocurrencies to be the case.
Out of curiosity I started learning its basics on Udemy course called Blockchain A-Z™: Learn How To Build Your First Blockchain. It was a turning point for me and I am happy I stumbled upon this course it made sense to me on its potential.
In my opinion, I still believe many cryptocurrencies are speculative but there are ones with attractive investment thesis. Anyway, this would be a different discussion.
After further reading on the topic of cryptocurrencies and particularly Bitcoin and Ethereum, here is what I learned.
In general, cryptocurrency is encrypted and secured (crypto) digital asset (currency) which can be used as a medium of exchange installed on the blockchain. Whereas the blockchain is a system installed on many computers across the world which enables decentralised secured network.
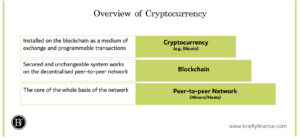
Now we know how they are connected. Let us know each work individually.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is one of the cryptocurrencies, it is a digital asset that work as a decentralised medium to exchange (that is why they compare it with gold and money). These coins are recorded on a database (blockchain on the network).
Bitcoin is programmed on a blockchain to transparently and securely record of payments
What is a Blockchain?
Blockchain on the other hand is an operating system that allows digital information to be recorded, distributed, and can’t be edited. What makes it unique is it holds an encrypted database that can’t be edited over a peer-to-peer network.
Two points to clarify.
- Digital information is not necessary a currency (which bitcoin is programmed as). It could be any form of transaction like votes, product inventories, deeds to homes, pictures/animation/videos (non-fundgeble tokens), and more.
- It is a secured operating system because it can be built on group of computers around the world which means when hacker wants to hack he has to influence every computer at the same time to succeed which is extremely difficult.

Attribution: The icons has been designed using resources from Flaticon.com
How is Bitcoin Related to Blockchain?
You may hear these words interchangeably and you want to know how Bitcoin is related to blockchain.
Let us think of it from the beginning, let us say there are 100 computers they want to host Bitcoin to make money from mining and transaction fees.
They will turn their computer into a host and install the blockchain operating system which then allows them to access the blockchain network of Bitcoin.
Now all these computers are working together to host Bitcoin through the blockchain.
This is not exactly how the technical aspect works but this is just an idea for you to know how they are related.
How does the Blockchain Work?
A blockchain is like a database that record transaction(s) per block (in our Bitcoin example it would hold the new coin generated and the transactions which are typically up to 1MB).
These blocks are generated by computers on the network through a protocol depending on the developer. For example, some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin would require the computers to solve a mathematical problem (Proof of work) others like Ethereum would require computers to show ownership of the coins (Proof of stake) whoever is faster wins the block reward.
Once the block is filled with transactions the computers get compensated and a new block start to get generated with the same protocol.
There is more depth in the matter which we will discuss later.
Below is an illustrative example of a blockchain with two first blocks and a summary description on the right.
How can we Benefit from the Blockchain?
- Blockchain enables decentralised networks which means platforms can be created without regulation overseeing them.
- It is very secured system, in order for hackers to do a transactions they are required to go through an extremely difficult process by manipulating multiple computers.
- Organisations can use the technology as part of their supply. It enables them to trace the goods and ensure that it is not being replaced or misused during each step of the process.
- Blockchain can carry any programmed file this means the potential is endless. For example, house ownership deeds, financial services transactions, ownership of collectible digital assets like NFTs and much more.
How a block is created?
A block is created with the following steps:
Step 1: A host/miner chooses transactions that happened and add them into the block they want to create.
Step 2: All computers on the network have to agree that the block is correct and should be added to the blockchain which is called a consensus protocol.
Step 3: Once the block is created the host/miner gets compensated.
Step 1: How do miners choose transactions?
Each host/miner has something called mempool attached to it. Mempool is where transactions are reflected and the fees that they are willing to compensate the miner.
Miners fill their block (usually with the higher fees transactions) and go to the next step to generate it and be the winner of the compensation along with the generated Bitcoin.
Step 2: The network has to agree about the transaction through the “consensus protocol” before the winner gets compensated with his block
Consensus protocol is a method to review and confirm the validity of the data where all the network agree that this created block is valid.
Because there is no regulator to accept or reject transactions this protocol is the way that makes blockchain to be a decentralised system where the agreement is automated and secured amongst all hosts/miners.
This help making sure that no one can hack and modify the information, and it also a checker that there will not be a double transactions.
Types of consensus protocols
There are many types of protocols that networks used for example Proof of work (PoW) is used by bitcoin and Proof of stake (PoS) used by Ethereum.
These protocol are how the system generate a block.
What is Proof of Work? (this protocol is used for Bitcoin to verify information and create block)
The proof of work protocol generates a block when a computer solves a mathematical equation “target” that is done by finding the “hash” through changing the “nonce” while the timestamp is moving.
I know this sentence may not be understood, but this is as simple as it gets.
Each block has a hash which is basically a cryptographical number (yes that is why it is cryptocurrency)
The hash changes whenever a nonce changes which is a range of numbers or the timestamp changes
There is a target to achieve to solve the equation, and once the computer solves it and find the right hash it will proceed and generate the block that included the transactions they had and also win the coin.
What is Proof of Stake?
Because there is high energy requirement energy for proof of work (According to the Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance (CCAF), Bitcoin currently consumes around 110 Terawatt Hours per year — 0.55% of global electricity production as referenced from Harvard Business Review May 2021) another known protocol has been used as an alternative which is proof of stake which consumes way much less energy.
Proof of stake requires the host to show that they have stake and ownership of a coin to become a validator (example for Ethereum it is 32 ETH). These validators are chosen randomly in the network to be able to generate the new coin with transactions that were collected from the mempool.
Step 3: How is that related to bitcoin? – What happens next?
Finally after the block is generated, the miner get compensated for the transaction fees (from transactions he chose earlier from the mempool) and receive his bitcoin.
Final Thoughts
And that is it, I know the topic has way much more depth in it. But my purpose here was to simplify the concept and get you ready to further read about the topic without getting confused with the terminologies. I hope I achieved that.
Related Posts:
- 6 Reasons Why Accounting is the Language of Business
- Is Accounting Hard? 6 Myths and their Realities
- Is Accounting a Good Career | Everything you Need to Know
Disclaimer: Above links are affiliate links and at no additional cost to you. I may earn a commission. Know that I only recommend products, tools, services and learning resources I’ve personally used and believe are genuinely helpful and relevant. It is not because of the small commissions I make if you decide to purchase them. Most of all, I would never advocate for buying something that you can’t afford or that you’re not yet ready to implement.